NEEP602 Course Notes (Fall 1997)
Resources from Space
Lecture #24: Been there! Done that! Bought the T-shirt!
Title: Lunar Base Activation
Notes:
General Assumptions
"Business" approach to lunar base activation (whether government or private)
o business plan development
o financial commitments
o coordination with and marketing to resource users
o detailed evaluation and characterization of the resource base
o definition of engineering design parameters for base and mining facilities
o mine planning
o development of base architecture and its activation sequence
o final definition of launch and support economics
o commitment to detail design, manufacture, and implementation
Lunar Base Design Goals
o Indefinite support of human activities
o Near term oxygen and hydrogen production
o Long term 3He production
o Long term production of basic material and food requirements
o Scientific exploration and use of the Moon
o Other?
Assumed frequency of launches of major support missions to the Moon
o One per lunar cycle
Engineering designs
o Finalized prior to initiation of base activation
Site of first base
o Best location for initial 3He production
o H2, H2O and O2 production can occur from regolith at any location
Assumed tours of duty for activation crews
o First year: 3 lunar cycles
o Second year: 6 lunar cycles
o Third and subsequent years: 12 lunar cycles
o Fifth year: option to settle
Work cycle
o 10 hour days and six day weeks
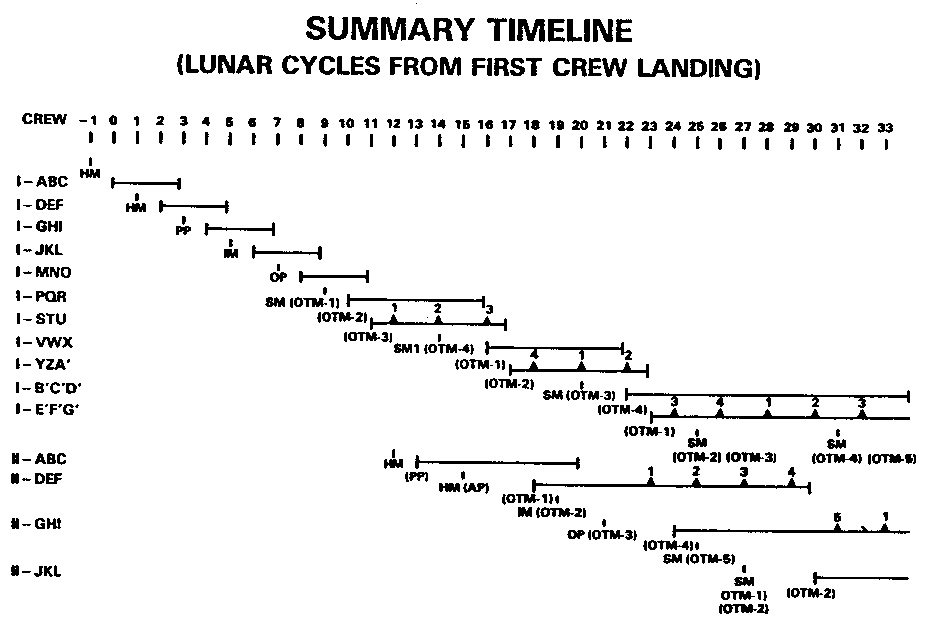 Summary Timeline for Activation Scenario (Schmitt, 1986)
HM: Habitation Module
PP: Power Plant
IM: Mining Plant
OP: Refining Plant
SM: Storage Module
OTM: Resource Transfer Module
Constraints on initial operations
Mission Rules (crew safety, ie, successful activation, emphasized in early phases)
o Maintain spare ascent module on surface until
base capable of supporting crews indefinitely
o Maintain inventory of consumables sufficient to
last two lunar cycles (one missed resupply)
o Other?
Environmental Considerations (see text from Neal, et al. 1988)
Landings
o First landing (Cycle -1): automated Habitation Module
o Second landing (Cycle 0): three person crew lands
o Third landing: second automated Habitation Module (Cycle 1)
o Fourth landing: second crew lands (Cycle 2) one cycle
before first crew rotates back to Earth
o Fifth landing: automated Power Plant (Cycle 3)
o Seventh landing: automated Mining Plant (Cycle 5)
o Ninth landing: automated Refining Plant (Cycle 7)
o Eleventh landing: automated Storage Module
with first Volatile Transfer Module (Cycle 9)
o First volatile shipment: Cycle 12
Crew consumables
o Early Phases: Minimum inventory capable of supporting base
population for two lunar cycles on full rations (one resupply missed)
o Later Phases: Phase in lunar production until indefinite
support possible from lunar resources
Power production
o Early Phases: solar energy/battery/RTG and/or fuel cell based
o Mid Phases (O2 and H2 production): solar energy/fuel cell based
o Late Phases and Settlement: nuclear fission or
fusion based with solar energy and fuel cells for special purposes
Crew Selection
o Skill mix and cross-training
o Experience
o Physical capability
o Medical risk analysis?
o Psychological risk analysis?
o Physiological and psychological tolerance to space environment? Space Station tour?
o Other?
Risk/Productivity Management
o No long term stand-downs in launches to Moon
o Physician on crew anytime six or more present
o Injury or illness treated at the base with replacement
by extension of tour of another qualified individual
o Crew selection
o Fail to operate/fail to manual/fail to safe equipment design
o Design facilities for internal diagnostics, rapid
inspection, rapid repair, and rapid upgrade
o Establish predictive (vibration, ultrasound, electrical, x-ray, etc.)
and preventive maintenance (pre-design life replacement) designs and systems
o Inventory all discarded or unused materials
o Dust management emphasis
o Solar flare risk management design and planning
o Design space suits with 1/2 the weight, 4 times the
hand and overall mobility, and 100 times the life of the Apollo suits
o Design lunar surface vehicles with solar particle
event protection and crew consumables
o Other?
Habitation
Summary Timeline for Activation Scenario (Schmitt, 1986)
HM: Habitation Module
PP: Power Plant
IM: Mining Plant
OP: Refining Plant
SM: Storage Module
OTM: Resource Transfer Module
Constraints on initial operations
Mission Rules (crew safety, ie, successful activation, emphasized in early phases)
o Maintain spare ascent module on surface until
base capable of supporting crews indefinitely
o Maintain inventory of consumables sufficient to
last two lunar cycles (one missed resupply)
o Other?
Environmental Considerations (see text from Neal, et al. 1988)
Landings
o First landing (Cycle -1): automated Habitation Module
o Second landing (Cycle 0): three person crew lands
o Third landing: second automated Habitation Module (Cycle 1)
o Fourth landing: second crew lands (Cycle 2) one cycle
before first crew rotates back to Earth
o Fifth landing: automated Power Plant (Cycle 3)
o Seventh landing: automated Mining Plant (Cycle 5)
o Ninth landing: automated Refining Plant (Cycle 7)
o Eleventh landing: automated Storage Module
with first Volatile Transfer Module (Cycle 9)
o First volatile shipment: Cycle 12
Crew consumables
o Early Phases: Minimum inventory capable of supporting base
population for two lunar cycles on full rations (one resupply missed)
o Later Phases: Phase in lunar production until indefinite
support possible from lunar resources
Power production
o Early Phases: solar energy/battery/RTG and/or fuel cell based
o Mid Phases (O2 and H2 production): solar energy/fuel cell based
o Late Phases and Settlement: nuclear fission or
fusion based with solar energy and fuel cells for special purposes
Crew Selection
o Skill mix and cross-training
o Experience
o Physical capability
o Medical risk analysis?
o Psychological risk analysis?
o Physiological and psychological tolerance to space environment? Space Station tour?
o Other?
Risk/Productivity Management
o No long term stand-downs in launches to Moon
o Physician on crew anytime six or more present
o Injury or illness treated at the base with replacement
by extension of tour of another qualified individual
o Crew selection
o Fail to operate/fail to manual/fail to safe equipment design
o Design facilities for internal diagnostics, rapid
inspection, rapid repair, and rapid upgrade
o Establish predictive (vibration, ultrasound, electrical, x-ray, etc.)
and preventive maintenance (pre-design life replacement) designs and systems
o Inventory all discarded or unused materials
o Dust management emphasis
o Solar flare risk management design and planning
o Design space suits with 1/2 the weight, 4 times the
hand and overall mobility, and 100 times the life of the Apollo suits
o Design lunar surface vehicles with solar particle
event protection and crew consumables
o Other?
Habitation
 Something better than Apollo (NASA photo)
Something better than Apollo (NASA photo)
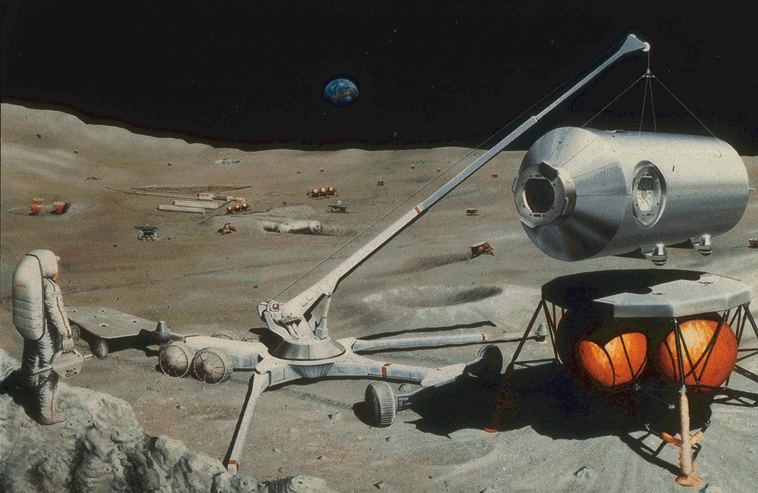 Deployment of Habitation Module (NASA Art)
o Design facilities for indefinite life, including in situ
maintenance, repair, and upgrade
o Design facilities and equipment against dust penetration
o Establish predictive and preventive maintenance designs and systems
o Use habitat and rover design and operational procedures to
protect against solar particle events
o Provide live, electronic views of the base and its setting
o Provide for recreational EVA
Deployment of Habitation Module (NASA Art)
o Design facilities for indefinite life, including in situ
maintenance, repair, and upgrade
o Design facilities and equipment against dust penetration
o Establish predictive and preventive maintenance designs and systems
o Use habitat and rover design and operational procedures to
protect against solar particle events
o Provide live, electronic views of the base and its setting
o Provide for recreational EVA
 Lunar recreation? (NASA art)
o Other?
Base planning
o The architectural layout of the base core will be final before the first landing
o The base will be located so as to easily support initial mining and
processing activities and to provide long term support for regional mining activities
o Landing and launch operations will be located and designed
so as to not disrupt other activities
o Landers and resource transfer modules will be
accessible to refueling and resource transfer facilities
o Roads and walkways will be stabilized
o Other?
Science Objectives
o Extend scientific knowledge of the Moon, particularly
as it relates to the Earth and the Solar System
o Conduct astronomical sensing
o Use the Moon-Earth system as a gravitational sensor
o Conduct resource exploration
o Investigate human adaptation to the lunar surface environment
(one-sixth gravity, radiation, dust, day-night cycles,
lack of Schumann resonance, psychological stress)
o Until a permanent scientific staff or full automation of
facilities is possible, science activities will be limited
o Facilities should be immune from disturbances resulting from base and mining activities
o Other?
Agriculture
Lunar recreation? (NASA art)
o Other?
Base planning
o The architectural layout of the base core will be final before the first landing
o The base will be located so as to easily support initial mining and
processing activities and to provide long term support for regional mining activities
o Landing and launch operations will be located and designed
so as to not disrupt other activities
o Landers and resource transfer modules will be
accessible to refueling and resource transfer facilities
o Roads and walkways will be stabilized
o Other?
Science Objectives
o Extend scientific knowledge of the Moon, particularly
as it relates to the Earth and the Solar System
o Conduct astronomical sensing
o Use the Moon-Earth system as a gravitational sensor
o Conduct resource exploration
o Investigate human adaptation to the lunar surface environment
(one-sixth gravity, radiation, dust, day-night cycles,
lack of Schumann resonance, psychological stress)
o Until a permanent scientific staff or full automation of
facilities is possible, science activities will be limited
o Facilities should be immune from disturbances resulting from base and mining activities
o Other?
Agriculture
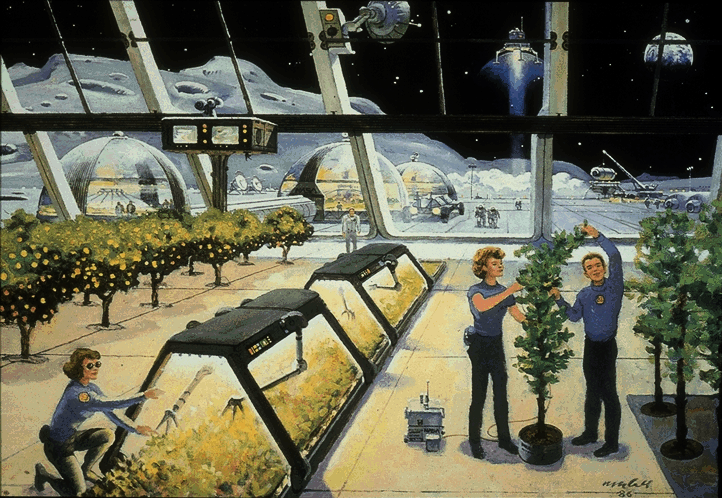 Agricultural Facility (NASA Art) What is missing?
o High priority in order to reduce cost of base support and demonstrate self-sufficiency
o Lighting design must protect crops from radiation while maximizing use of solar energy
o Hydroponics versus traditional techniques must be evaluated
o Biological waste must be recycled
o Evaluate the need for soil/water additives over time
o Evaluate export economics
o Other?
Readaptation
o After full adaptation to one-sixth gravity, persons
scheduled to return to Earth's gravity will need several
weeks of special physical exercises and physiological stress pre-conditioning.
Other Early Considerations
o Plant Activation and Test
- Power Plant
- Mining Plant
- Refining Plant
o Storage Module Placement
o Resource Transport Module Placement
Agricultural Facility (NASA Art) What is missing?
o High priority in order to reduce cost of base support and demonstrate self-sufficiency
o Lighting design must protect crops from radiation while maximizing use of solar energy
o Hydroponics versus traditional techniques must be evaluated
o Biological waste must be recycled
o Evaluate the need for soil/water additives over time
o Evaluate export economics
o Other?
Readaptation
o After full adaptation to one-sixth gravity, persons
scheduled to return to Earth's gravity will need several
weeks of special physical exercises and physiological stress pre-conditioning.
Other Early Considerations
o Plant Activation and Test
- Power Plant
- Mining Plant
- Refining Plant
o Storage Module Placement
o Resource Transport Module Placement
o By-product storage
Integrated Operations
o May require split shifts two person teams
Management
o Technical and Operational Management: Lunar Base managers
o Logistic Coordination: Lunar Base and Earth based managers
o Overall Management: Earth-based until full logistics
self-sufficiency exists at the lunar base
Issues for trade-off studies and modeling to select best
technical approach to mining (i.e., rectilinear vs. spiral):
o logistical support costs
o estimated cost/tonne comparing apples with apples
o percentage minable left unmined vs. marginal costs to mine
o use of supplemental equipment, e.g., bulldosers to clear boulder fields.
o Other?
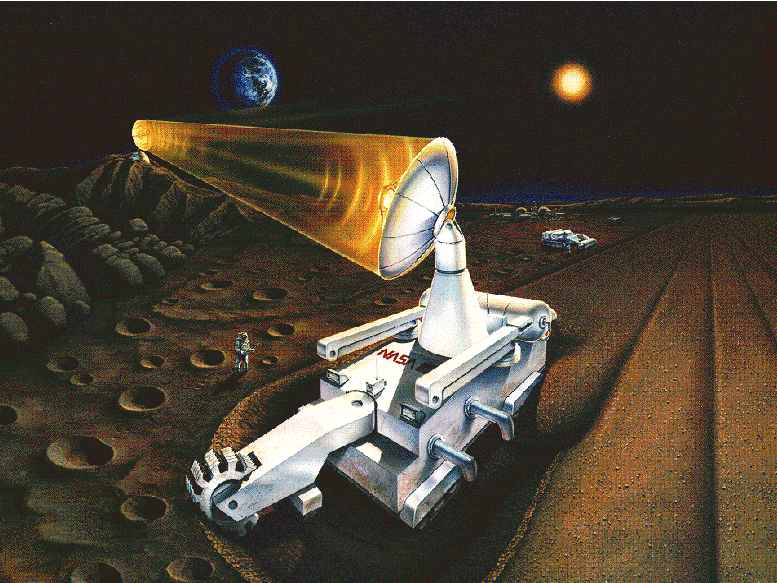 Wisconsin Mark II miner concept
Requirements for conducting day to day mining operations
o logistical support
o systems monitoring
o teleoperations
o maintenance
o balance between extraction and refining and
shipment/storage
Issues for day to day mining operations (see text in Lecture 19 from Neal, et al., 1988)
Wisconsin Mark II miner concept
Requirements for conducting day to day mining operations
o logistical support
o systems monitoring
o teleoperations
o maintenance
o balance between extraction and refining and
shipment/storage
Issues for day to day mining operations (see text in Lecture 19 from Neal, et al., 1988)
Questions:
1. Sketch and annotate a possible architectural layout for a lunar base supporting both spiral 3He mining and a science station.
2. Discuss the trade-off issues to be considered in selecting spiral mining versus rectilinear mining (see Lecture #19 as well).
3. Discuss how to provide solar particle event protection to a two person lunar exploration expedition traveling with an Apollo-like lunar rover. Assume 30 minutes notice before arrival of intense particle flux.
Text:
Neal., et al., 1988, pages 38-46
References:
Mendell, W.W., 1985, editor, The First Conference on Lunar Bases and Space Activities of the 21st Century, Chapter 6, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston.
Mendell, W.W., 1992, editor, The Second Conference on Lunar Bases and Space Activities of the 21st Century, Chapters 2,3,6, and 7, NASA Conference Publication 3166, 667-672.
Neal., V., et al., 1988, Extravehicular Activity at a Lunar Base, Report on Advanced Extravehicular Activity Systems Requirements Definition Study, NASA-17779.
Schmitt, H.H., 1986, Lunar base network activation scenario, in Final Report: Lunar Power Systems, P 2-1 to 1-43, NASA-JSC Contract NAS9-17359.
Schmitt, H.H., 1992, The real world and Lunar base activation scenarios, in The Second Conference on Lunar Bases and Space Activities of the 21st Century, edited by W.W. Mendell, NASA Conference Publication 3166, 667-672.
 |
|
University of Wisconsin Fusion Technology Institute · 439 Engineering Research Building · 1500 Engineering Drive · Madison WI 53706-1609 · Telephone: (608) 263-2352 · Fax: (608) 263-4499 · Email: fti@engr.wisc.edu |
Copyright © 2003 The Board of
Regents of the University of Wisconsin System.
For feedback or accessibility issues, contact
web@fti.neep.wisc.edu.
|